Thoracic strengthening exercises target the mid-back region, enhancing spinal stability and posture. They improve mobility, reduce back pain, and boost athletic performance by addressing muscle imbalances.
Importance of Thoracic Spine Health
The thoracic spine, as the longest segment of the spine, plays a critical role in maintaining posture, facilitating movement, and protecting internal organs; Poor thoracic spine health can lead to issues like kyphosis, herniated discs, or chronic pain, significantly impacting daily activities and athletic performance. A strong, mobile thoracic spine reduces the risk of injuries and improves overall spinal stability. Neglecting this area can result in compensatory movements, strained muscles, and limited mobility. Maintaining thoracic spine health is essential for preventing long-term complications and ensuring optimal physical function.
Benefits of Thoracic Strengthening
Thoracic strengthening enhances spinal stability, improves posture, and reduces back pain. It boosts mobility, allowing for better movement patterns and athletic performance. Strengthening the thoracic spine helps prevent injuries, alleviates muscle imbalances, and supports overall core stability. Improved thoracic function can also enhance breathing and reduce strain on other spinal regions. Regular exercises promote long-term spinal health, making daily activities and sports more efficient. Stronger thoracic muscles contribute to better body mechanics, reducing the risk of chronic pain and improving quality of life. Incorporating these exercises into a fitness routine offers numerous benefits for both corrective and preventative spinal care.

Common Thoracic Strengthening Exercises
Common exercises include thoracic extensions, rotations, and spinal mobilization. These movements improve mobility, posture, and spinal stability, often using tools like resistance bands or dumbbells.
Thoracic Extension Exercises
Thoracic extension exercises focus on strengthening the muscles of the mid-back, improving spinal mobility, and enhancing posture. These exercises involve arching or extending the thoracic spine, often performed while standing or seated. A common example is the thoracic extension stretch, where one leans forward with arms outstretched or clasps hands behind the head to gently arch backward. Proper technique is crucial to avoid neck strain, ensuring movement originates from the mid-back. Regular practice can help reduce kyphosis, improve respiratory function, and alleviate upper back tension. Incorporating these exercises into a routine promotes better spinal alignment and reduces the risk of injuries. Start with gentle repetitions and progress gradually for optimal results.
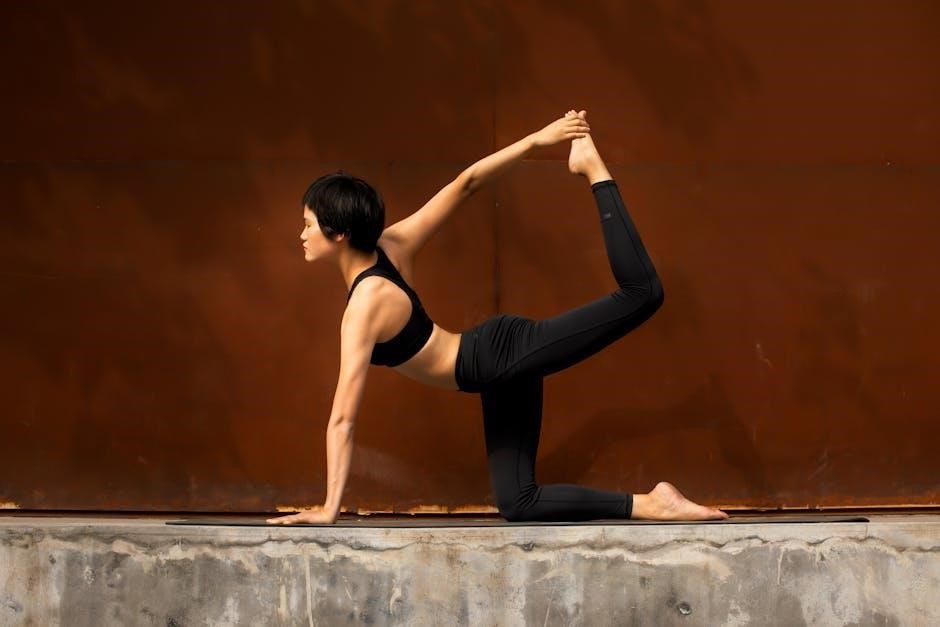
Thoracic Rotation Exercises
Thoracic rotation exercises aim to enhance spinal mobility and strengthen rotational movement in the mid-back. These exercises often involve twisting the torso while maintaining a neutral spine. A popular example is the “thread the needle” pose, performed on all fours by rotating the spine and reaching one arm through the gap. Another effective exercise is seated thoracic rotation, where one twists while holding a light weight or resistance band. These movements improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and enhance athletic performance. Proper form is essential to avoid strain, ensuring the rotation comes from the thoracic spine, not the neck or lower back. Incorporating these exercises can help restore natural spinal movement and reduce the risk of injury. Start with controlled, gentle rotations and gradually increase depth as mobility improves.
Thoracic Spine Mobilization Techniques
Thoracic spine mobilization techniques focus on improving flexibility and reducing stiffness in the mid-back region. These exercises often involve gentle, controlled movements to enhance joint mobility and relieve tension. Techniques such as thoracic rotations, side-to-side motions, and spinal extensions are commonly used. For example, the “thread the needle” exercise on all fours helps improve rotational mobility, while self-mobilization with a foam roller or hands can release tightness. These methods are particularly beneficial for individuals with limited thoracic movement or those recovering from spinal injuries. Regular practice can restore natural spinal mechanics, enhance posture, and reduce the risk of back pain. Consistency is key to achieving long-term improvements in thoracic mobility and overall spinal health.
Exercise Techniques and Safety
Proper posture and controlled movements are crucial for safe thoracic exercises. Start with light weights, gradually increasing intensity, and use tools like resistance bands for support.
Proper Posture During Exercises
Maintaining proper posture is essential for effective and safe thoracic strengthening exercises. Keep your spine in a neutral position, avoiding excessive arching or slouching. Engage your core muscles to support your lower back and ensure stability. When performing exercises like thoracic extensions or rotations, focus on moving from the mid-back rather than the neck or shoulders. Use a mirror or feedback from a trainer to monitor your alignment. Avoid rounding your shoulders or tilting your head excessively. Instead, keep your chin slightly tucked to maintain cervical spine alignment. Proper posture ensures that the target muscles are engaged and reduces the risk of injury. Progress gradually to more challenging movements while maintaining form.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When performing thoracic strengthening exercises, avoid rounding your shoulders or using momentum to lift weights, as this can strain the neck and shoulders. Do not arch your lower back excessively, as it can lead to injury. Ensure movements are controlled and slow, focusing on the mid-back muscles. Overstretching or bouncing during exercises can cause discomfort or harm. Neglecting proper breathing techniques is another common mistake; exhale during the exertion phase for stability. Avoid pushing past pain or discomfort, as this may indicate improper form. Lastly, do not skip the warm-up or cool-down routines, as they are crucial for muscle preparation and recovery. Awareness of these mistakes helps in maximizing the effectiveness of the exercises while minimizing the risk of injury.
Progression of Exercises
Progressing thoracic strengthening exercises involves gradually increasing intensity, resistance, or range of motion. Start with bodyweight exercises like thoracic extensions or rotations, ensuring proper form. As strength improves, add resistance using bands, dumbbells, or machines. Incorporate dynamic movements, such as rotational exercises with weights, to challenge stability and mobility. Increase the number of sets, reps, or duration as tolerance builds. Advanced routines may include compound movements like bent-over rows or rotational lifts. Always monitor form and adjust progressively to avoid plateaus or injury. Consistency and gradual overload are key to achieving long-term improvements in thoracic strength and spinal mobility. Proper progression ensures continued growth and prevents stagnation in training.

Targeted Muscle Groups

Thoracic strengthening exercises engage muscles like the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, rhomboids, and erector spinae, enhancing spinal stability and promoting proper posture and movement patterns.
Muscles Involved in Thoracic Strengthening
Thoracic strengthening exercises engage several key muscle groups, including the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, rhomboids, and erector spinae. These muscles play a crucial role in stabilizing the thoracic spine and improving posture. The latissimus dorsi helps in spinal extension and rotation, while the trapezius and rhomboids contribute to scapular stability, which is essential for proper thoracic movement. The erector spinae muscles run along the spine, aiding in extension and rotation. Strengthening these muscles enhances spinal stability, reduces the risk of injury, and improves overall athletic performance. Weakness in these areas can lead to poor posture and increased susceptibility to back pain.
Role of Scapular Muscles in Thoracic Stability
The scapular muscles, including the trapezius, rhomboids, levator scapulae, and serratus anterior, play a vital role in thoracic stability. These muscles help stabilize the scapula, which directly influences the thoracic spine’s positioning and movement. The trapezius and rhomboids work to retract and depress the scapula, maintaining proper alignment and reducing strain on the thoracic spine. The serratus anterior facilitates scapular rotation, enhancing thoracic mobility. Weakness in these muscles can lead to poor posture, altered movement patterns, and increased risk of injury. Strengthening the scapular muscles is essential for achieving optimal thoracic stability and overall spinal health.

Exercise Equipment and Tools
Resistance bands, dumbbells, and specialized equipment like Swiss balls are commonly used for thoracic strengthening. These tools enhance muscle engagement and improve spinal stability during exercises.
Use of Resistance Bands
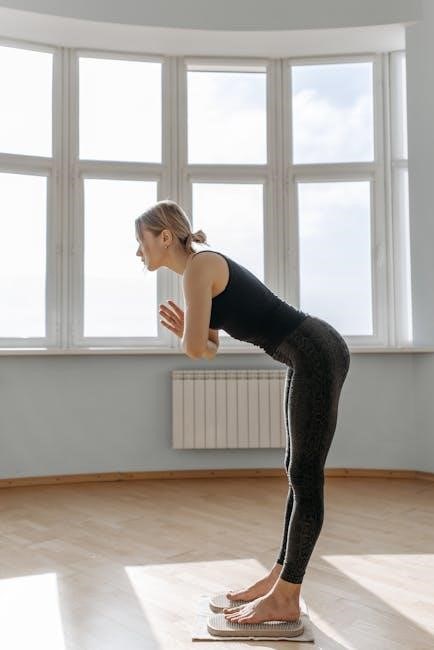

Resistance bands are a versatile and portable tool for thoracic strengthening. They provide consistent resistance, helping to build strength and improve mobility. For thoracic exercises, bands can be anchored to a stable object or used in seated or standing positions. Common exercises include chest presses, rows, and rotational movements. Bands are lightweight and easy to adjust, making them suitable for all fitness levels. Proper form is essential to avoid injury and maximize effectiveness. Using resistance bands regularly can enhance thoracic stability and posture. They are also cost-effective and space-saving, ideal for home or travel workouts. Incorporating bands into routines promotes consistent progression and muscle engagement.
Exercises with Dumbbells or Weights
Dumbbells and weights are effective tools for thoracic strengthening, offering resistance to build muscle endurance and improve spinal stability. Exercises like bent-over rows, lateral raises, and shoulder presses target the thoracic region. When using weights, maintaining proper form is crucial to prevent injury. Starting with lighter weights and gradually increasing intensity helps build strength safely. Dumbbell exercises can be performed seated or standing, depending on the movement. They enhance posture, reduce back pain, and improve overall upper body alignment. Incorporating weight-based exercises into routines promotes muscle balance and long-term spinal health. Consistency and focus on technique ensure optimal results and lasting thoracic stability;

Exercise Routines for Different Needs
Exercise routines can be tailored to suit individual needs, such as fitness level, injury recovery, or specific goals. Beginner-friendly routines focus on foundational strength, while advanced options incorporate progressive overload and complex movements. Post-surgical or rehabilitative routines prioritize gentle mobilization and stability. Customizing exercises ensures safe and effective progression, addressing unique requirements and promoting long-term spinal health and overall well-being.
Beginner-Friendly Exercises
Beginner-friendly thoracic strengthening exercises focus on gentle movements to improve posture, mobility, and reduce back pain. Start with thoracic extensions by sitting or standing tall, interlacing fingers behind your head, and gently arching backward. Another simple exercise is the cat-cow stretch, which involves kneeling and alternating between rounding and arching your spine. Seated thoracic twists, where you twist your torso while keeping your feet on the floor, are also effective. These exercises are low-impact, easy to learn, and can be done at home with minimal equipment. Consistency is key to building strength and improving spinal mobility over time. Always consult a professional before starting any new routine.
Advanced Thoracic Strengthening Routines
Advanced thoracic strengthening routines incorporate dynamic movements and resistance to challenge the mid-back muscles. Exercises like weighted thoracic rotations, using resistance bands or dumbbells, enhance strength and stability. Dynamic twists, such as rotating while holding a weight, improve rotational power. High-to-low cable pulls target the thoracic spine and scapular muscles, promoting better posture. Advanced cat-cow variations with resistance bands add intensity to spinal mobility. These routines are designed for individuals with a solid foundation in basic exercises, aiming to elevate strength, flexibility, and athletic performance. Always focus on proper form to avoid injury and maximize results. Gradually increase resistance to continue building thoracic strength and stability over time.

Additional Tips for Success
Consistency is key; perform exercises 3-4 times weekly for optimal results. Start with light resistance and gradually increase intensity. Focus on proper form to prevent injury and maximize effectiveness. Incorporate flexibility exercises to maintain range of motion. Listen to your body and rest when needed. Track progress to stay motivated and adjust routines as strength improves. A well-rounded approach ensures sustainable thoracic strength and overall spinal health.
Incorporating Stretching After Strengthening
Incorporating stretching after thoracic strengthening exercises is essential for maintaining flexibility and reducing muscle soreness. Gentle stretching helps elongate muscles, improving range of motion and preventing stiffness. Focus on static stretches for the thoracic spine, such as seated thoracic twists or cat-cow stretches, holding each for 20-30 seconds. Dynamic stretches, like arm circles or side bends, can also enhance mobility. Avoid bouncing during stretches to prevent injury. Additionally, using mild heat before stretching can increase tissue elasticity, making stretches more effective. Consistently combining stretching with strengthening ensures a balanced routine, promoting long-term spinal health and overall athletic performance. Proper technique is crucial to maximize benefits.
Importance of Consistency and Frequency
Importance of Consistency and Frequency
Consistency and frequency are crucial for effective thoracic strengthening. Regular exercises ensure progressive overload, leading to muscle adaptation and spinal stability. Aim for 2-3 sessions weekly, gradually increasing intensity. Frequency helps maintain muscle memory and posture improvements. Over time, consistent practice enhances thoracic mobility and reduces injury risk. Incorporate exercises like thoracic extensions and rotations, adjusting frequency as fitness levels improve. Tracking progress ensures sustained motivation and proper technique. A well-structured routine with consistent effort yields long-term benefits for spinal health and overall physical performance. Stay committed to achieve optimal results and prevent setbacks. Proper scheduling ensures exercises become a sustainable part of your fitness journey. Consistency is key to achieving and maintaining a strong, healthy thoracic spine. Frequency supports continuous improvement and adaptation, making it essential for a successful strengthening program.
Thoracic strengthening exercises are vital for spinal health and posture. For comprehensive guides, refer to recommended PDF resources and expert references for detailed routines and techniques.
Final Thoughts on Thoracic Strengthening
Thoracic strengthening exercises are essential for improving spinal health, enhancing athletic performance, and maintaining proper posture. By incorporating exercises like extensions, rotations, and mobilizations, individuals can address muscle imbalances and reduce the risk of injury. Consistency is key, as these exercises require regular practice to yield noticeable results. Additionally, pairing strengthening routines with stretching can promote flexibility and reduce muscle soreness. For those seeking structured guidance, downloadable PDF resources provide comprehensive workout plans tailored to different fitness levels. Remember, thoracic strengthening is a long-term investment in spinal stability and overall well-being. Stay committed, and over time, you’ll experience improved mobility and reduced discomfort.
Recommended PDF Guides and References
Several high-quality PDF guides are available online, offering detailed thoracic strengthening exercise routines. These resources often include step-by-step instructions, illustrations, and progress tracking tools. Studies by authors like TE Andreeva and VA Parfenov highlight the effectiveness of targeted spine exercises. Additionally, resources from PhysioTools Ltd and Body Maintenance studio provide practical exercise plans for post-surgery recovery and spinal health. These guides are ideal for both beginners and advanced learners, ensuring a safe and structured approach to thoracic strengthening. Downloadable PDFs are convenient for personal use, allowing users to follow routines at home or in a gym setting. They often emphasize consistency and proper form for optimal results.
